Incandescent light bulbs are a common type of lighting. They produce light through a filament heated to a high temperature.
These bulbs have been around for over a century. You find them in homes, offices, and many other places. They work by passing electricity through a thin wire inside the bulb. The wire, or filament, gets very hot and glows, producing light.
While they are simple and inexpensive, they are not very energy-efficient. Incandescent bulbs convert most of the energy they use into heat, not light. This makes them less efficient compared to newer types of bulbs. In this blog, we will explore how incandescent bulbs work, their advantages, and their drawbacks. This will help you understand more about this classic lighting choice.

Credit: www.architecturaldigest.com
Introduction To Incandescent Bulbs
The most long-lasting and oldest form of technology for lights, one of the most ubiquitous, is the incandescent light bulb. Incandescent lights produce light through electricity passed through a thin filament of wire and then heated to cause it to glow. Incandescent lights have a yellowish, warm glow and have become a staple for use in residential, office, and even decor spaces. Incandescent lights, despite them being phased out with newer, efficient options, have a lasting presence in technology for lights.
Brief History of Incandescent Bulbs
The creation of the incandescent light bulb began in the early 19th century. There were many inventors who played with electric lights, but refinishing the technology in 1879 is credited to Thomas Edison.
- Early Innovations – Scholars such as Humphry Davy and Joseph Swan developed early forms of incandescent lights.
- The Breakthrough – Edison’s carbon filament bulb added efficiency and durability, and soon enough, electric lights entered widespread use.
- Evolution Over Time – Incandescent lights have evolved with newer, new materials, such as tungsten filaments, that make them brighter and durable.
Though less applicable with increased use of LEDs and CFLs with efficiency, incandescent lights played a key role in transforming artificial lights forever.
Basic Definition of an Incandescent Bulb
An incandescent bulb is a plain, ordinary light bulb that generates light through heat and electrical resistance. It consists of:
- Glass Bulb – Protects and disperses the light.
- Tungsten Filament – A thin filament that glows when electrified and then heats.
- Metal Base – Connects with source of electricity
- Inert Gas (in a few bulbs) – Protects filament and prolongs its life span.
Once electricity flows through the filament, it becomes thousands of degrees hot, producing visible light. Incandescence is its proper name, and that is why such a bulb releases light and heat.

Credit: www.delmarfans.com
How Incandescent Bulbs Work
Incandescent light bulbs utilize light through the heating of a thin filament of a metal till it glows. Simple and efficient, technology is over a hundred years old.
- Electricity Flows through Filament – Once a switch is thrown, electricity runs through a thin filament of tungsten in a case of glass.
- The Filament Gains Heat – Resistance in filament creates enough heat to warm filament to about 2,500–3,000°C (4,500–5,400°F).
- Light Emitted – Under such a high temperature, filament turns white and glows, creating light.
But, incandescent bulbs lack efficiency in terms of using energy. Nearly 90% of consumed energy is consumed in creating heat and about 10% in creating light. That’s one of the most important reasons for them to be replaced with LED and CFL lights.
Types Of Incandescent Bulbs
Different types of incandescent bulbs, each with a specific purpose for use.
1. Common Incandescent Bulbs
- Most widespread in use in residential and work environments.
- Emit a yellowish, warm glow with a cozy atmosphere.
- Exist in a variety of forms and dimensions for use in a variety of types of fixtures.
- Cost-effective but short-lasting, lasting about 750 to 1,000 hours at best.
- Have a high consumption level in terms of modern alternatives such as LEDs or CFLs.
2. Specialty Incandescent Bulbs
They have specific applications and have a specific shape, form, and colors for them.
- Appliance Bulbs – For use in microwaves, fridges, and ovens and must function in high and low temperatures.
- Decorative Bulbs – Applied in chandeliers, accent lights, and string lights, in clear, frosted, and colored.
- Miniature Bulbs – Applied in medical instruments, medical equipment, and flashlights for use in small spaces.
- Heavy-Duty Bulbs – For use in factory settings, offering added durability in terms of vibrational and hostile environments.
Though specialty incandescent bulbs can be less convenient and expensive in relation to traditional ones, in special cases lights of any other sort won’t function
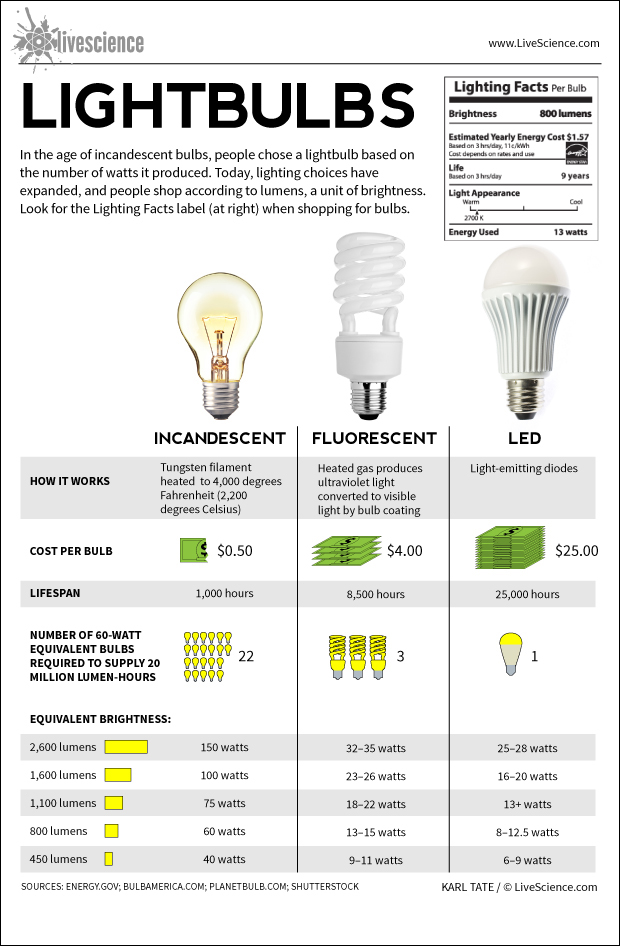
Credit: www.livescience.com
Advantages Of Incandescent Bulbs
Incandescent light bulbs provide warm, natural light. They are affordable and easy to replace. Ideal for creating a cozy atmosphere.
Cost Efficiency
Incandescent bulbs are very affordable. They are cheaper than many other types of bulbs. This makes them a good choice for people on a budget. You can buy them almost anywhere. They are easy to find in stores. Also, they do not need special fixtures. You can use them in most lamps and sockets. This saves money on buying new fixtures. They also work well with dimmer switches. This means you can adjust the light level. It makes it easier to save energy and money.
Color Rendering
Incandescent bulbs provide excellent color rendering. Colors look natural under their light. This is important for tasks where color matters. For example, in art studios or makeup application. They create a warm light. This makes rooms feel cozy and inviting. Many people prefer this warm light over other types. It is easy on the eyes. This can reduce eye strain. Incandescent bulbs are good for reading and working. They help you see colors as they really are. This is why they are still popular in many homes.
Disadvantages Of Incandescent Bulbs
Incandescent bulbs waste a lot of energy. They turn most energy into heat, not light. This makes them less efficient than other bulbs. Energy costs can be higher due to this wastage. LED and CFL bulbs use less power. This makes them better for saving energy.
Incandescent bulbs burn out quickly. They last around 1,000 hours. This means you need to replace them often. LED bulbs last much longer. They can last up to 25,000 hours. Frequent replacement adds to the cost of using incandescent bulbs. It also means more waste.
Comparing Incandescent With Other Bulbs
LED bulbs are very energy-efficient. They use less power than incandescent bulbs. This means lower electricity bills. LED bulbs also last much longer. You may need to replace them less often. These bulbs stay cool, making them safer. They come in many colors and shapes. This offers more choices for your home.
CFL bulbs are another energy-saving option. They use less power than incandescent bulbs too. CFL bulbs last longer than incandescent ones, but not as long as LEDs. They can save you money over time. Some people find the light of CFL bulbs too harsh. They also contain a small amount of mercury, so handle with care. Dispose of them properly to avoid harm to the environment.
Applications Of Incandescent Bulbs
Decades have seen widespread use of incandescent bulbs for their warm glow, cost-effectiveness, and ease of use. Even with alternatives taking over, they enjoy continued use in many environments.
1. Home Application
They can be seen in most homes, providing a warm and welcoming atmosphere.
- Living Rooms & Bedroom – Their yellowish, soft glow creates a relaxing and cozy atmosphere.
- Table & Floor Lamps – Best for reading, studying, and accent lights.
- Kitchen & Bathroom Lighting – Often installed in ceiling lights and vanities.
- Corridors & Entranceways – Offer quick lights when powered on.
They are inexpensive, simple to install, and readily available, and therefore a first preference for many homeowners.
2. Commercial & Hospitality Sector
Restaurants, shops, and entertainment spaces utilize incandescent bulbs for enhancing atmosphere.
- Shops & Retail Outlets – Employed in shop lights for showcasing goods.
- Restaurants & Cafes – With a warm glow, they make for a cozy and welcoming meal.
- Lounges & Bars – Contribute to a relaxed and intimate atmosphere for guests.
- Theater & Concert Halls – Employed in theater lights, spotlight, and decor.
- Small Business & Hotels – Selected for cost-effectiveness and ease of maintenance.
- Aesthetic value and warm glow make them a first preference in commercial and hospitality settings.
3. Specialty & Decorative Uses
Certain incandescent lights have specialized applications in addition to general use.
- Decorative String Lights – For weddings, events, and patios.
- Appliance Lights – In fridges, microwaves, and ovens for temperature tolerance.
- Art & Photography Studios – In specific photographic illuminating sets for a warm glow.
- Holiday & Festive Lights – Incandescent technology continues to be in use in most decorative and Christmas lights. Such specific lights will continue to be utilized where such specific capabilities are desired.
Future Of Incandescent Bulbs
Many countries have set rules to limit incandescent bulbs. These bulbs use a lot of energy. The goal is to save power and protect our planet. Some places have full bans. Others have rules that make it hard to sell these bulbs. This means fewer people can buy them. New laws will likely make these rules stricter.
Energy-saving bulbs are a good choice. LED bulbs last longer and use less power. They are better for the environment. Compact Fluorescent Lamps (CFLs) are another option. They save energy too. These bulbs help lower electricity bills. Using these bulbs means fewer greenhouse gases. This helps our planet stay healthy. Choose smart for a brighter future.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Are Incandescent Light Bulbs?
Incandescent light bulbs produce light by heating a filament. They are known for their warm light. They are less energy-efficient compared to LEDs and CFLs.
How Do Incandescent Bulbs Work?
Incandescent bulbs work by passing electric current through a tungsten filament. The filament heats up and glows, producing light.
Are Incandescent Bulbs Energy-efficient?
No, incandescent bulbs are not energy-efficient. They convert only about 10% of energy into light. The rest is wasted as heat.
What Is The Lifespan Of Incandescent Bulbs?
Incandescent light bulbs typically last around 750 to 2,000 hours. Their lifespan is shorter compared to LEDs and CFLs.
Conclusion
Incandescent light bulbs have a rich history and many applications. They produce warm, inviting light. Though less efficient, they remain popular for ambiance. Understanding their function helps in making informed choices. While newer technologies emerge, incandescent bulbs hold their charm.
Their simplicity and affordability are unmatched. Knowing their pros and cons is essential. Choose wisely based on your needs and preferences.

My name is Mahi Uddin, and I’m a blog writer with over two years of experience specializing in creating engaging, informative content using AI tools. I contribute to InExDecor.com, where I share creative ideas and practical tips for transforming interior and exterior spaces into beautiful, functional environments. With a passion for storytelling and a knack for blending creativity with technology, I strive to craft blogs that not only inform but also inspire readers. When I’m not writing, you can find me exploring design trends or enjoying a good book with a cup of coffee.








