Designing a garden can be both exciting and rewarding. It transforms outdoor spaces into beautiful, functional areas.
Creating a garden involves more than just planting flowers. It’s about planning, choosing the right plants, and knowing how to arrange them. A well-designed garden reflects your style and meets your needs. Whether you want a space for relaxation, entertaining guests, or growing vegetables, thoughtful design is key.
This guide will help you understand the basics of garden design. From selecting the right plants to arranging them for maximum impact, you’ll learn how to create a garden that thrives. Ready to turn your outdoor space into a stunning garden? Let’s dive in and discover the steps to design a beautiful garden.
Credit: www.prettypurpledoor.com
How to Design a Garden: 8 Expert Tips
1. Choosing A Location
Designing a garden begins with choosing the right location. This crucial step affects the overall success of your garden. The location determines sunlight exposure, soil quality, and accessibility. By selecting the best spot, you ensure your plants thrive. This guide will help you understand the key factors to consider when choosing a location for your garden.
Sunlight Requirements
Sunlight is essential for plant growth. Different plants need different amounts of sunlight. Understanding these needs is vital for successful garden planning.
Here are some key points to consider:
- Full Sun: Plants needing full sun require at least 6-8 hours of direct sunlight daily. Examples include tomatoes, peppers, and roses.
- Partial Sun: These plants thrive with 3-6 hours of sunlight. Suitable for plants like lettuce, spinach, and ferns.
- Shade: Shade-loving plants need less than 3 hours of direct sunlight. Ideal for hostas, ferns, and certain flowers.
Observe your garden area throughout the day. Note the spots receiving full sun, partial sun, and shade. This observation helps in the proper garden layout and plant selection. A simple table can help you keep track:
| Area | Sunlight Exposure |
|---|---|
| North Corner | Full Sun (6-8 hours) |
| East Side | Partial Sun (3-6 hours) |
| South Corner | Shade (<3 hours) |
Proper sunlight exposure ensures healthy plants and a vibrant garden. Consider these sunlight requirements during your landscape design phase.
Soil Quality
Soil quality is another crucial factor in garden planning. Different plants thrive in different soil types. Understanding your soil helps in the proper plant selection and garden maintenance.
Consider these soil types:
- Clay Soil: Heavy and dense, retains water but drains slowly. Suitable for plants like daylilies and asters.
- Sandy Soil: Light, drains quickly but needs frequent watering. Ideal for root vegetables like carrots and potatoes.
- Loamy Soil: Balanced mixture of sand, silt, and clay. Excellent drainage and nutrient retention. Perfect for most plants.
Testing your soil is simple. Take a small sample and observe its texture:
- If it feels sticky and forms a ball, it’s clay.
- If it feels gritty and falls apart, it’s sandy.
- If it feels smooth and holds shape but crumbles easily, it’s loamy.
Consider using raised beds or adding compost to improve soil quality. Proper soil preparation enhances plant health and growth. Implementing effective irrigation systems also helps in maintaining soil moisture.
Understanding soil quality is key to a successful garden layout. Follow these gardening tips to create a thriving garden environment.
2. Setting Goals
Designing a garden is an exciting and creative process. One of the first steps in garden planning is setting goals. Establishing clear goals will guide your decisions on garden layout, planting design, and other landscape design elements. By setting goals, you can ensure your garden meets your aesthetic preferences and functional needs.
Aesthetic Appeal
Aesthetic appeal is a crucial aspect of garden design. It defines how your garden looks and feels. Consider what kind of atmosphere you want to create. Do you prefer a modern, minimalist garden or a lush, cottage-style garden? Your choices in plant selection, garden features, and layout will influence the overall look.
To achieve a visually pleasing garden, consider the following tips:
- Color Scheme: Choose a color scheme that complements your home and surroundings. Use a mix of flowers, foliage, and garden features to create harmony.
- Texture and Form: Combine plants with different textures and forms. Mix grasses, shrubs, and flowers to add depth and interest.
- Focal Points: Include focal points such as a fountain, statue, or a unique plant. These elements draw the eye and add structure to the space.
A balanced garden layout enhances aesthetic appeal. Arrange plants in layers, placing taller plants at the back and shorter ones in the front. This creates a sense of depth. Additionally, consider the seasons. Choose plants that bloom at different times of the year to ensure year-round beauty.
Functional Spaces
Functional spaces are essential in garden planning. Think about how you will use your garden. Do you need space for outdoor living, such as dining or relaxation? Or do you want to grow vegetables and herbs? Identifying these needs will help you design a garden that works for you.
Here are some ideas for creating functional spaces:
- Outdoor Living Areas: Designate areas for seating, dining, and socializing. Use patio furniture, pergolas, or gazebos to create comfortable spaces.
- Paths and Walkways: Include paths to connect different areas of your garden. Use materials like gravel, stone, or wood for a natural look.
- Vegetable and Herb Gardens: Allocate space for growing your own produce. Raised beds or container gardens are great for small spaces.
Utilize space efficiently. For small gardens, vertical gardening can be a great solution. Use trellises or wall planters to maximize space utilization. Sustainable gardening practices, such as composting and rainwater harvesting, can also enhance functionality.
By combining aesthetic appeal with functional spaces, you can create a garden that is both beautiful and practical. Thoughtful garden planning and design will ensure your garden meets your needs and brings you joy.
Best Book: How to Design a Garden
3. Selecting Plants
Designing a garden is a fulfilling task that can bring beauty and tranquility to your outdoor space. A critical step in garden planning is selecting the right plants. The plants you choose will determine the overall look, maintenance needs, and biodiversity in your garden. It is essential to consider factors like climate, soil type, and the amount of sunlight your garden receives. Let’s explore two key aspects of plant selection: native species and seasonal blooms.
Native Species
Choosing native species is a smart move for any garden. Native plants are adapted to the local climate and soil conditions. They require less water and maintenance, making them ideal for sustainable gardening. Here are some benefits of using native species in your garden layout:
- Low Maintenance: Native plants thrive with minimal care.
- Water Efficiency: They need less watering, saving you time and resources.
- Support Local Wildlife: Native species attract birds, butterflies, and beneficial insects.
- Resilience: These plants are more resistant to local pests and diseases.
Incorporating native species into your landscape design can enhance the outdoor aesthetics and support biodiversity in gardens. Here is a table showcasing some popular native plants for different regions:
| Region | Popular Native Plants |
|---|---|
| Midwest | Purple Coneflower, Black-Eyed Susan |
| Southwest | California Poppy, Desert Marigold |
| Northeast | Eastern Red Columbine, New England Aster |
| Southeast | Coreopsis, Blazing Star |
When planning your garden, consider using these native plants to create a sustainable and vibrant space.
Seasonal Blooms
Including seasonal blooms in your garden design ensures that your outdoor space remains colorful throughout the year. Different plants bloom in various seasons, adding dynamic beauty to your garden layout. Here are some tips for selecting seasonal blooms:
- Spring Blooms: Look for plants like tulips, daffodils, and cherry blossoms. These flowers bring vibrant colors after winter.
- Summer Blooms: Roses, lilies, and sunflowers thrive in the summer heat. They add bright hues and a lively atmosphere.
- Autumn Blooms: Choose plants like chrysanthemums, asters, and marigolds. These blooms provide warm tones and complement the fall foliage.
- Winter Blooms: Consider hellebores, camellias, and winter jasmine. These plants offer beauty even in the colder months.
Creating a flower arrangement with seasonal blooms can enhance outdoor aesthetics year-round. Here is a simple table to help you plan for each season:
| Season | Recommended Plants |
|---|---|
| Spring | Tulips, Daffodils, Cherry Blossoms |
| Summer | Roses, Lilies, Sunflowers |
| Autumn | Chrysanthemums, Asters, Marigolds |
| Winter | Hellebores, Camellias, Winter Jasmine |
Consider these plants as you work on your garden planning. They will help you achieve a beautiful and dynamic garden throughout the year.

Credit: littleterracedhouse.com
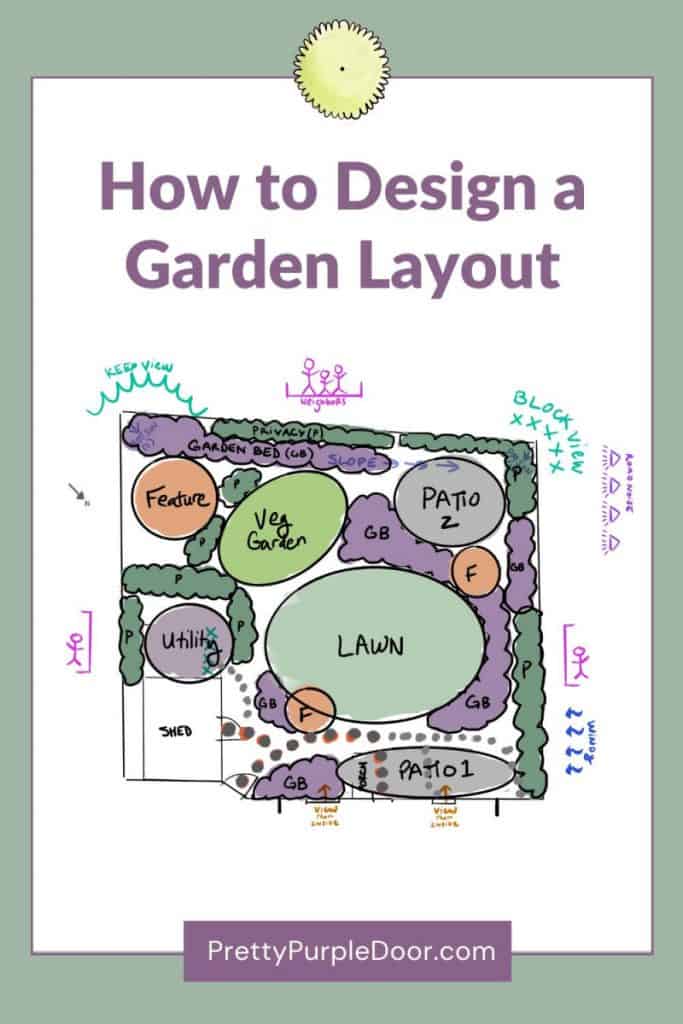
4. Creating Layouts
Creating a beautiful garden starts with thoughtful planning and design. A well-designed layout can transform your outdoor space into a tranquil retreat or a vibrant gathering spot. The key to a successful garden layout is to divide the space into zones, plan pathways and borders, and consider the aesthetics and functionality of the garden.
Garden Zones
Dividing your garden into zones helps you organize the space effectively. Each zone can serve a different purpose, making the garden more functional and enjoyable. Consider the following zones for your garden:
- Seating Area: A place to relax and enjoy the garden. Include comfortable furniture and shade.
- Vegetable Plot: Ideal for growing your own produce. Requires good soil preparation and sunlight.
- Flower Beds: Plant seasonal flowers for year-round color. Plan your planting schemes to ensure blooms in different seasons.
- Play Area: A safe space for children to play. Consider soft grass or a sandpit.
- Water Feature: Adds tranquility and attracts wildlife. Can be a pond or a small fountain.
To create a cohesive garden layout, think about the flow between these zones. Use garden features like trellises, hedges, or stone walls to define different areas. This helps in creating a sense of order and enhances the garden aesthetics.
Here’s a simple table to help you plan your garden zones:
| Zone | Purpose | Key Considerations |
|---|---|---|
| Seating Area | Relaxation | Furniture, Shade |
| Vegetable Plot | Growing Produce | Soil Preparation, Sunlight |
| Flower Beds | Color and Beauty | Planting Schemes, Seasonal Flowers |
| Play Area | Children’s Activities | Safety, Soft Ground |
| Water Feature | Tranquility | Water Source, Wildlife |
Pathways And Borders
Pathways and borders are crucial elements in garden design. They guide visitors through the garden and define different zones. Well-designed pathways enhance the landscape design and improve garden maintenance.
Consider the following tips for planning pathways:
- Material: Choose materials that complement your garden aesthetics. Options include gravel, stone, brick, or wood.
- Width: Ensure pathways are wide enough for easy movement. A minimum of 3 feet is recommended.
- Shape: Curved paths create a natural look, while straight paths are more formal.
- Lighting: Add lights along pathways for safety and ambiance in the evening.
Borders help to frame the garden and keep different zones distinct. They also prevent plants from encroaching onto pathways. For effective borders, use:
- Edging Plants: Low-growing plants like lavender or boxwood create neat edges.
- Hard Materials: Bricks, stones, or metal edging provide a clear boundary and are durable.
Incorporate sustainable gardening practices by using recycled materials for pathways and borders. This not only looks great but also helps the environment. Regular garden maintenance ensures pathways and borders remain in good condition, contributing to the overall beauty of your outdoor space.
5. Incorporating Features
Designing a garden involves more than just plant selection and garden layout. Incorporating features such as water elements and seating areas can enhance the overall outdoor aesthetics and functionality. These features not only add to the visual appeal but also provide a space for relaxation and enjoyment. Let’s explore how to include these elements in your garden planning.
Water Elements
Water elements can transform a simple garden into a tranquil oasis. The sound of running water can create a soothing atmosphere, making your garden a perfect spot for relaxation. Here are some ideas to consider:
- Fountains: Available in various designs, from modern to classic, fountains can be a focal point in your garden.
- Ponds: A pond can support aquatic plants and fish, adding biodiversity to your landscape design.
- Waterfalls: These can be integrated into ponds or standalone structures, providing a continuous flow of water.
- Birdbaths: Simple yet effective, birdbaths attract birds, adding life and movement to your garden.
When planning to incorporate water elements, consider the following factors:
| Factor | Considerations |
|---|---|
| Size | Ensure the water feature fits the scale of your garden layout. |
| Location | Place it where it can be seen and heard from various parts of the garden. |
| Maintenance | Choose features that match your garden maintenance capabilities. |
Water elements not only enhance outdoor aesthetics but also promote sustainable gardening by creating habitats for wildlife. Consider them an essential part of your garden planning process.
Seating Areas
Seating areas provide a place to relax, entertain, and enjoy your garden. They can be as simple or elaborate as you like. Here are some seating ideas to consider:
- Benches: Classic and versatile, benches can be placed in shaded spots or near focal points.
- Patios: A patio with comfortable seating can serve as an outdoor living room.
- Arbors and Pergolas: These structures can provide shade and a sense of enclosure for seating areas.
- Hammocks: Ideal for a casual and relaxed vibe, hammocks can be hung between trees or posts.
When designing seating areas, consider these design principles:
- Comfort: Choose seating that is comfortable and inviting.
- Accessibility: Ensure seating areas are easily accessible from different parts of the garden.
- View: Place seating where you can enjoy the best views of your garden features.
- Shade: Provide shade with umbrellas, pergolas, or natural tree cover.
Seating areas can be enhanced with hardscaping ideas such as stone pathways, wooden decks, or brick patios. These elements add structure and definition to your garden layout. They also make your outdoor space more functional and enjoyable. Properly planned seating areas will encourage you and your guests to spend more time outdoors, appreciating the beauty of your garden.
6. Sustainable Practices
Designing a garden is both an art and a science. Sustainable practices ensure that your garden thrives while preserving the environment. These practices enhance soil health, conserve water, and reduce waste. Adopting sustainable methods like organic gardening and composting can make your garden a green haven. Let’s explore how to incorporate these practices into your garden design.
Organic Gardening
Organic gardening focuses on growing plants without synthetic fertilizers or pesticides. This method is not only eco-friendly but also promotes healthier plant growth. By using natural materials, you can create a self-sustaining garden ecosystem.
Here are some key components of organic gardening:
- Soil Preparation: Enrich the soil with organic matter like compost or manure. This improves soil structure and fertility.
- Plant Selection: Choose plants that are well-suited to your local climate and soil. Native plants often require less maintenance.
- Raised Beds: Consider using raised beds for better drainage and soil control. These beds can be filled with organic soil mixes.
- Pest Control Methods: Use natural pest control methods such as beneficial insects or companion planting. Avoid chemical pesticides.
- Seasonal Planting: Plant according to the seasons to ensure that your plants thrive. Rotate crops to maintain soil health.
Incorporating these elements into your garden layout can lead to a more sustainable gardening practice. Let’s look at a table that summarizes the benefits of organic gardening:
| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Healthier Plants | Plants grow stronger without synthetic chemicals. |
| Soil Health | Organic matter improves soil structure and fertility. |
| Environmental Protection | Reduces chemical runoff and pollution. |
| Cost-Effective | Uses natural resources, reducing the need for expensive chemicals. |
Composting Techniques
Composting is a key component of sustainable gardening. It involves recycling organic waste into valuable fertilizer for your garden. This practice reduces landfill waste and enriches the soil with essential nutrients.
Here are some effective composting techniques:
- Backyard Composting: Create a compost pile in your yard. Add kitchen scraps, garden clippings, and leaves. Turn the pile regularly to speed up decomposition.
- Vermicomposting: Use worms to break down organic waste. This method is great for small spaces and produces nutrient-rich worm castings.
- Tumbler Composting: Use a compost tumbler for faster results. Tumblers are easy to turn and can produce compost in a few weeks.
- Trench Composting: Bury organic waste directly in the garden. This method is simple and improves soil structure directly in the planting area.
Each technique has its own benefits. Let’s summarize them in a table:
| Technique | Benefits |
|---|---|
| Backyard Composting | Large capacity, improves soil, reduces waste. |
| Vermicomposting | Efficient, produces high-quality compost, suitable for small spaces. |
| Tumbler Composting | Fast results, easy to use, contained system. |
| Trench Composting | Direct soil improvement, low maintenance, no equipment needed. |
Adopting these composting techniques can significantly enhance your garden’s sustainability. They ensure a continuous supply of natural fertilizer, reducing the need for synthetic products. Sustainable practices like organic gardening and composting create a healthier, more resilient garden.
7. Maintenance Tips
Designing a garden is a rewarding experience, but it comes with ongoing responsibilities. Proper garden maintenance ensures your outdoor space remains beautiful and healthy throughout the seasons. Effective maintenance includes regular watering, pruning, and weeding. These tasks might seem daunting, but with the right schedule and techniques, you can keep your garden in top shape with ease.
Watering Schedule
A consistent watering schedule is crucial for the health of your garden. Plants need water to grow, bloom, and produce fruit. Here’s how you can manage your watering routine:
- Early Morning or Late Afternoon: Water your plants during these times to reduce water evaporation.
- Check Soil Moisture: Use your finger or a moisture meter. Water when the top inch of soil is dry.
- Deep Watering: Ensure water reaches the roots. Shallow watering can lead to weak root systems.
- Drip Irrigation: Consider using drip irrigation for consistent water delivery and reduced waste.
Different plants have varying water needs. Group plants with similar water requirements together in your garden layout. This practice, known as hydrozoning, makes watering more efficient. Here’s a simple table to help you understand the water needs of common garden plants:
| Plant Type | Watering Frequency |
|---|---|
| Succulents and Cacti | Once every 2 weeks |
| Vegetables | 2-3 times per week |
| Flowering Plants | 1-2 times per week |
| Lawns | 3 times per week |
Pruning And Weeding
Pruning and weeding are essential for maintaining garden aesthetics and plant health. Regularly trimming plants encourages new growth and removes dead or diseased parts. Here’s how to approach these tasks effectively:
- Pruning:
- Use Sharp Tools: Sharp pruners make clean cuts and prevent plant damage.
- Prune in the Right Season: Prune flowering plants after they bloom. Trim fruit trees in late winter or early spring.
- Remove Dead or Diseased Branches: This prevents the spread of disease and encourages healthy growth.
- Weeding:
- Weed Regularly: Remove weeds before they set seed. This keeps them from spreading.
- Use Mulch: Mulch suppresses weeds and retains soil moisture. It is a key part of sustainable gardening.
- Hand-Pull or Use Tools: Hand-pull small weeds. Use a hoe or weeding tool for larger ones.
Pruning and weeding not only improve the appearance of your garden but also promote plant health. Regular maintenance can prevent overgrowth and make your garden planning more manageable. By incorporating these practices into your routine, you will enjoy a thriving, well-maintained outdoor space.
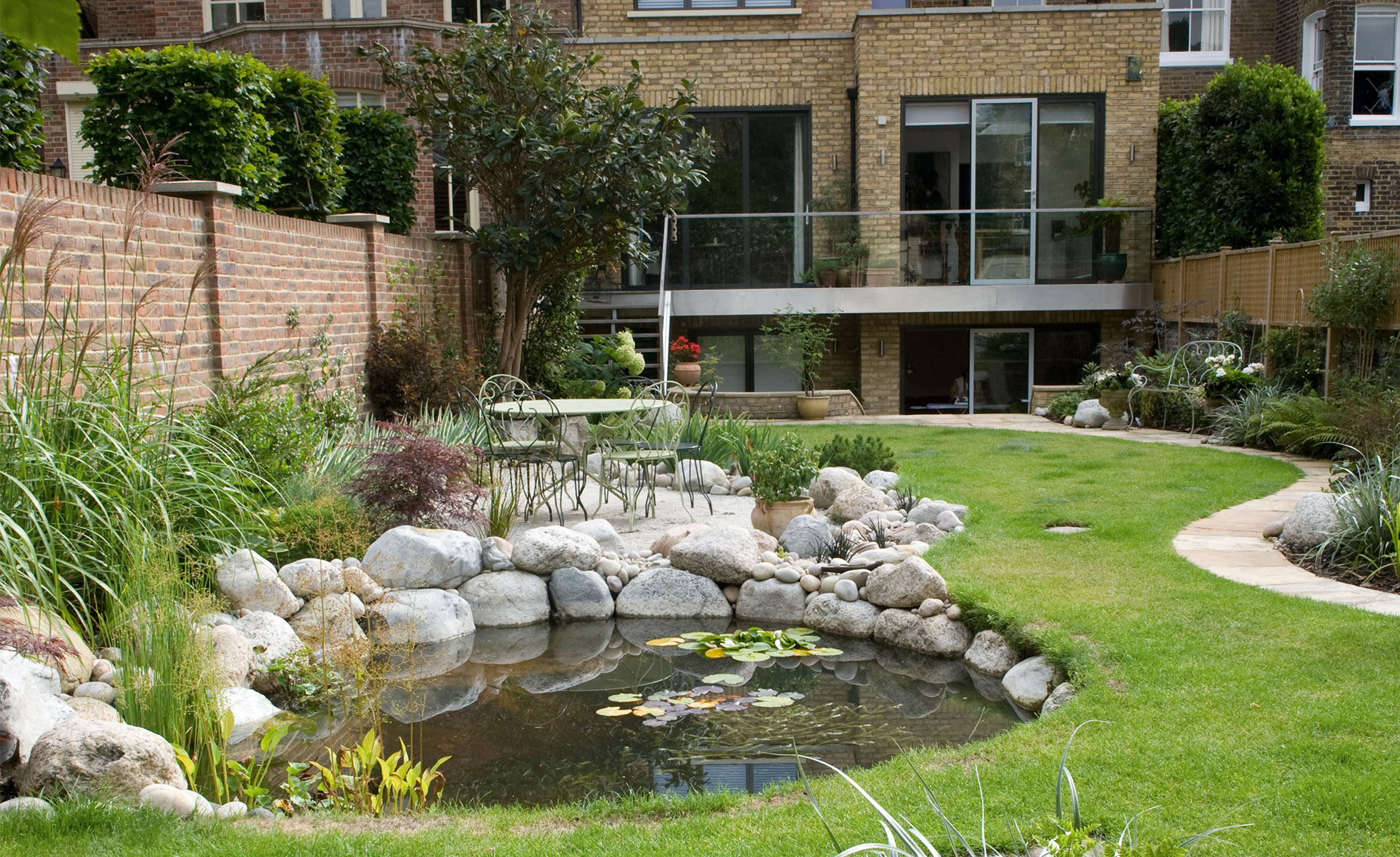

Credit: www.realhomes.com
8. Seasonal Adjustments
Designing a garden involves more than just planting flowers and shrubs. It’s about understanding the seasonal changes and making necessary adjustments. Seasonal adjustments ensure that your garden remains vibrant and healthy throughout the year. Here, we’ll explore how to prepare your garden for winter and the best practices for spring planting.
Winter Preparations
Winter can be harsh on your garden. Proper preparation is essential for protecting your plants and soil. Start by cleaning up your garden. Remove dead plants, leaves, and debris. This helps prevent pests and diseases.
Soil Preparation is crucial. Add compost or organic matter to improve soil health. This enriches the soil with nutrients that plants need to survive the cold months. Cover the soil with mulch to retain moisture and regulate temperature.
- Protect sensitive plants: Use burlap or frost cloth to cover delicate plants.
- Inspect irrigation systems: Drain and shut off systems to prevent freezing.
- Garden Features: Clean and store garden tools and decorations.
Winter is also a good time to plan your Landscape Design. Think about the changes you want to make. Consider new plants, different layouts, and additional garden features.
Here’s a handy table for winter preparations:
| Task | Description |
|---|---|
| Soil Preparation | Add compost and mulch |
| Protect Plants | Cover sensitive plants with burlap |
| Inspect Irrigation | Drain and shut off systems |
| Clean Up | Remove dead plants and debris |
Spring Planting
Spring is the perfect time to refresh your garden. Start with a good Soil Preparation. Test your soil’s pH and add necessary amendments. This ensures a healthy start for your plants.
Next, focus on Flower Selection. Choose flowers that thrive in your climate. Mix perennials and annuals for year-round color. Consider the Garden Layout. Plant taller plants at the back and shorter ones at the front. This creates a layered look.
Here are some Planting Tips for spring:
- Plant in groups: Clusters of plants look more natural and are easier to maintain.
- Water wisely: Use drip irrigation systems to save water and ensure plants get the moisture they need.
- Mulch: Apply mulch to retain soil moisture and prevent weeds.
Don’t forget about Garden Maintenance. Regularly check for pests and diseases. Prune plants to encourage growth and remove dead or damaged parts.
Spring is also a great time to add new Garden Features. Consider adding a birdbath, a bench, or new pathways to enhance your garden’s Outdoor Aesthetics.
Use this checklist for spring planting:
- Test soil and add amendments
- Select suitable flowers and plants
- Plan garden layout
- Install or check irrigation systems
- Mulch and maintain the garden
Frequently Asked Questions
What Are The Basics Of Garden Design?
Start with a plan. Consider sunlight, soil, and water needs. Choose plants that suit your climate. Create focal points for visual interest.
How Do I Choose Plants For My Garden?
Select plants based on your climate, soil type, and sunlight. Consider plant height, color, and blooming season for variety.
What Are Common Garden Design Mistakes?
Overcrowding plants, ignoring sunlight needs, and poor soil preparation are common mistakes. Plan space and light requirements carefully.
How Can I Make My Garden Low Maintenance?
Choose native plants, use mulch to retain moisture, and install an efficient irrigation system. Minimize lawn areas for less upkeep.
Conclusion
Creating your dream garden can be simple and rewarding. Start small. Plan carefully. Choose plants that thrive in your climate. Add personal touches like paths or water features. Regular maintenance keeps your garden beautiful. Enjoy the process and watch your garden grow.
Your unique oasis awaits. Happy gardening!

My name is Mahi Uddin, and I’m a blog writer with over two years of experience specializing in creating engaging, informative content using AI tools. I contribute to InExDecor.com, where I share creative ideas and practical tips for transforming interior and exterior spaces into beautiful, functional environments. With a passion for storytelling and a knack for blending creativity with technology, I strive to craft blogs that not only inform but also inspire readers. When I’m not writing, you can find me exploring design trends or enjoying a good book with a cup of coffee.







